Recent updates to Google’s search algorithms (named Panda and
Penguin) have caused many website owners to doubt Google’s “don’t be
evil” attitude. Before you start hating Google for your website’s change
in rankings, let’s take a look at why Google makes the decisions it
does.
The first item in Google’s philosophy is “Focus on the user and all else will follow.” Google works hard to provide a search engine that will give searchers the best information available on the web relative to their search terms. Google is working to serve web users, not just website owners. It follows then, that Google would adjust its algorithms to bring higher quality content to the top of its search rankings.
“I’m THE Big Fat Panda”
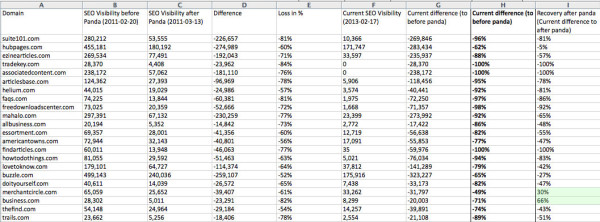
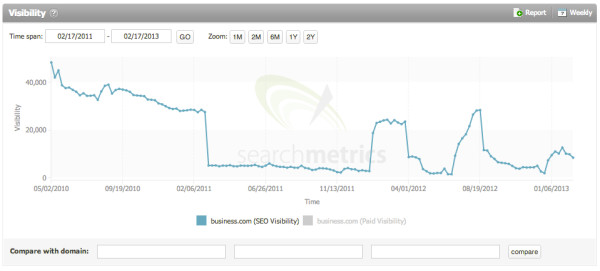
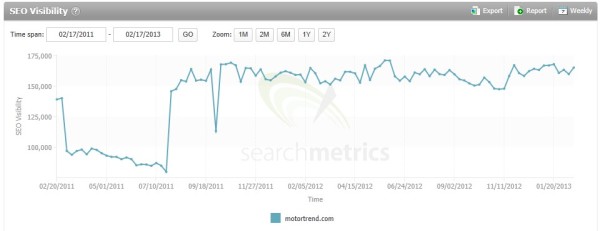
In late February 2011, Google rolled out the first of its major algorithm updates, dubbed, “Google Panda.” The main intent of Google Panda was to increase user experience by lowering the ranking of websites with “low-quality” or “thin” content. Conversely, websites with high-quality, unique content would be rewarded with an increased ranking. This change affected nearly 12% of all Google searches.
By April 2011, this update had rolled out to encompass all English queries, and by August, Google Panda had gone international, including all non-English queries.
To figure out what makes a site “high-quality” in Panda’s algorithms, let’s take a look at four main points:
Is the site trustworthy?
A trustworthy site has information written by someone who knows what he or she is talking about (an expert). It includes facts and figures that people find believable and wouldn’t report to Google for suspicious activity.
Does the site have original content?
A website should have new information on each page that isn’t redundant and hasn’t been gathered from another source.
Is there value?
The more value a website has, the better rankings Google will give it. Valuable websites have information that is interesting, complete, comprehensive and shareable.
Does the site have lots of spam?
Websites with lots of ads and “click here” banners are not considered to be high-quality sites. This update also has to do with a site’s page layout. An update to the algorithm in October 2012 targets pages with too many ads above the fold.
“There’s a New Sheriff in Town”
In April of 2012, Google rolled out an update code-named “Penguin”. Due to this update, various methods of SEO are no longer desirable and can actually hurt search rankings. If you are trying any of the following, you should probably stop right away.
Keyword Stuffing
This is exactly what it sounds like. Stuffing a webpage with applicable keywords, hiding text behind images, and going crazy with meta tags. Not only is this annoying to your page’s visitors, it will provide no advantage on almost any current search engine. And Google will actually penalize your site in the rankings if they detect keyword stuffing. Remember, it’s about quality content, not quantity.
Cloaking
Cloaking is a slightly more advanced method of “black-hat” SEO, but this also will not increase your Google page rank. This is where a script on your website delivers a different version of your page to the search engine’s “crawler” than the webpage that your actual visitors see. With this, you can send whatever keywords you want to increase rankings, yet have something totally different pop up when users click through to your page. Sneaky workarounds like this no longer get results.
Link Schemes
You may have received emails from so-called SEO companies, or other businesses like yours, offering a link swapping service. It sounds a lot like the old chain mail postcards kids used to send around in grade school. “Send out ten postcards and get 8 billion in return.” In link schemes, you post other people’s links on your website in return for their posting your links on their websites. The idea is Google will see that many websites refer to your website, giving you a better ranking in search results. Penguin looks for websites participating in link schemes and penalizes them for manipulating the search results.
Duplicate Content
Akin to keyword stuffing, duplicate content involves deliberately posting the same content on multiple pages within a website. The intention of duplicate content is to appear to have a plethora of pages and information on certain topics, and thereby garner higher rankings in Google searches. Again, Penguin identifies sites that have high levels of duplicate content and penalizes them in search results. This has caused difficulties for sites with multiple similar products. With quality product descriptions however, penalization can be avoided.
Exact Match Domain Update
On Friday, September 28, Google released an update to its algorithm that affects “exact-match” domains in the search results. The purpose of this update is to reduce the number of websites that rank for searches just because their domain is the same as a particular search. For example, if someone Googles “pet groomers in Chicago”, one of the websites in the search results might be “www.petgroomersinchicago.com”. And that site may have been ranking in the search results because of its name, but not because it was a quality website. This algorithm update is supposed to change that.
So remember, the key to a lasting presence in the search results is to have high quality content. It’s still good to include useful links and applicable keywords, but it should all be legitimate content. Hopefully the tips included here are helpful to you. If you have more questions, contact us here at Wallaroo Media!
Reference:-http://wallaroomedia.com/why-did-i-lose-my-rankings-in-google/
EBriks Infotech:-SEO India
The first item in Google’s philosophy is “Focus on the user and all else will follow.” Google works hard to provide a search engine that will give searchers the best information available on the web relative to their search terms. Google is working to serve web users, not just website owners. It follows then, that Google would adjust its algorithms to bring higher quality content to the top of its search rankings.
“I’m THE Big Fat Panda”
In late February 2011, Google rolled out the first of its major algorithm updates, dubbed, “Google Panda.” The main intent of Google Panda was to increase user experience by lowering the ranking of websites with “low-quality” or “thin” content. Conversely, websites with high-quality, unique content would be rewarded with an increased ranking. This change affected nearly 12% of all Google searches.
By April 2011, this update had rolled out to encompass all English queries, and by August, Google Panda had gone international, including all non-English queries.
To figure out what makes a site “high-quality” in Panda’s algorithms, let’s take a look at four main points:
Is the site trustworthy?
A trustworthy site has information written by someone who knows what he or she is talking about (an expert). It includes facts and figures that people find believable and wouldn’t report to Google for suspicious activity.
Does the site have original content?
A website should have new information on each page that isn’t redundant and hasn’t been gathered from another source.
Is there value?
The more value a website has, the better rankings Google will give it. Valuable websites have information that is interesting, complete, comprehensive and shareable.
Does the site have lots of spam?
Websites with lots of ads and “click here” banners are not considered to be high-quality sites. This update also has to do with a site’s page layout. An update to the algorithm in October 2012 targets pages with too many ads above the fold.
“There’s a New Sheriff in Town”
In April of 2012, Google rolled out an update code-named “Penguin”. Due to this update, various methods of SEO are no longer desirable and can actually hurt search rankings. If you are trying any of the following, you should probably stop right away.
Keyword Stuffing
This is exactly what it sounds like. Stuffing a webpage with applicable keywords, hiding text behind images, and going crazy with meta tags. Not only is this annoying to your page’s visitors, it will provide no advantage on almost any current search engine. And Google will actually penalize your site in the rankings if they detect keyword stuffing. Remember, it’s about quality content, not quantity.
Cloaking
Cloaking is a slightly more advanced method of “black-hat” SEO, but this also will not increase your Google page rank. This is where a script on your website delivers a different version of your page to the search engine’s “crawler” than the webpage that your actual visitors see. With this, you can send whatever keywords you want to increase rankings, yet have something totally different pop up when users click through to your page. Sneaky workarounds like this no longer get results.
Link Schemes
You may have received emails from so-called SEO companies, or other businesses like yours, offering a link swapping service. It sounds a lot like the old chain mail postcards kids used to send around in grade school. “Send out ten postcards and get 8 billion in return.” In link schemes, you post other people’s links on your website in return for their posting your links on their websites. The idea is Google will see that many websites refer to your website, giving you a better ranking in search results. Penguin looks for websites participating in link schemes and penalizes them for manipulating the search results.
Duplicate Content
Akin to keyword stuffing, duplicate content involves deliberately posting the same content on multiple pages within a website. The intention of duplicate content is to appear to have a plethora of pages and information on certain topics, and thereby garner higher rankings in Google searches. Again, Penguin identifies sites that have high levels of duplicate content and penalizes them in search results. This has caused difficulties for sites with multiple similar products. With quality product descriptions however, penalization can be avoided.
Exact Match Domain Update
On Friday, September 28, Google released an update to its algorithm that affects “exact-match” domains in the search results. The purpose of this update is to reduce the number of websites that rank for searches just because their domain is the same as a particular search. For example, if someone Googles “pet groomers in Chicago”, one of the websites in the search results might be “www.petgroomersinchicago.com”. And that site may have been ranking in the search results because of its name, but not because it was a quality website. This algorithm update is supposed to change that.
So remember, the key to a lasting presence in the search results is to have high quality content. It’s still good to include useful links and applicable keywords, but it should all be legitimate content. Hopefully the tips included here are helpful to you. If you have more questions, contact us here at Wallaroo Media!
Reference:-http://wallaroomedia.com/why-did-i-lose-my-rankings-in-google/
EBriks Infotech:-SEO India